Special Education
History
In the late 1700's Jean Mare Gaspard Itard looked for new methods to teach mental retardation.
In 1817 the first school for deaf as established in Hartford, Connecticut.
In 1966 the Bureau of Education for the Handicapped was established.
In 1968 the Special Olympics was created by Eunice Kennedy Shriver.
In 1971 Pennsylvania Association for Retarded Children won a case vs. Common wealth of Pennsylvania.
In 1973 Vocational Rehabilitation Act was created.
In 1976 All-Handicapped Children's Act was created.
In 1990 the Americans with Disabilit Act was created.
In 1997 the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act created.
In 2004 IDEA was amended.
Disability Areas
Autism- Developmental disability that affects social interaction and verbal and non-verbal communication.
Deafness- Hearing impairment that severely impairs linguistic information.
Hearing Impairment- Loss of hearing either permanent or fluctuating.
Mental Retardation- Intellectual functioning existing with deficits in adaptive behavior.
Multiple Disabilities- A combination of impairments that causes severe education problems.
Orthopedic Impairment- Impairments involving a missing limb or ones caused by diseases, like cerebral palsy.
Other Health Impairments- These include limited strength, vitality, or alertness caused by chronic or acute health problems.
Tourette Syndrome- Neurological disorder that includes repetitive involuntary movements.
Emotional Disturbance- Children who have mood related disabilities such as schizophrenia.
Specific Learning Disabilities- Disorder in one or more basic psychological processes.
Speech or Language Impairment- A speaking disorder involving articulation such as stuttering.
Traumatic Brain Injury- Acquired injury to the brain caused by an outside physical force.
Visual Impairment- A sight impairment that includes partial sight loss or blindness.
Pervasive Developmental Disorder- A delay in social, language, motor or cognitive development.
Assessment
Notice and parent consent must be given in order to evaluate the child. More than one procedure must be done to determine a child's eligibility. A child must be assessed in all areas of suspected disabilities. An IEP team must be formed in order for eligibility to be determined. Once an IEP is made teachers and other school personnel are required to follow the correctional procedures.
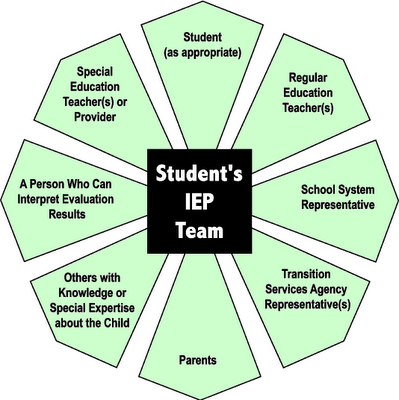
IEP
Members of a Pre-referral team must meet and fill out an IEP to help a child with a disability to receive the proper help.

Teaching Methodology
Teachers should review a students record and ask any specialists for help on anything they may not understand. Some things that teachers may need to do consist of: Give students more time on tests, break tasks into smaller units, provide directions verbally and in writing, Have a peer or classroom assistant take notes or write answers on tests, provide tutors in order to individualize teaching, provide audio-taped textbooks, and providing supplementary video materials that relate to classroom topics. Teachers should teach study skills, organizational skills, and learning strategies in a way that the students can understand. Teachers and parents need to become partners in teaching a child with a disability and communicate on a regular basis. It is important that teachers learn all they can about any disabilities that their students may have. When teachers have the awareness of the disability and also what is listed on the IEP it will help them to teach the student with the best outcome.
Resource Citation